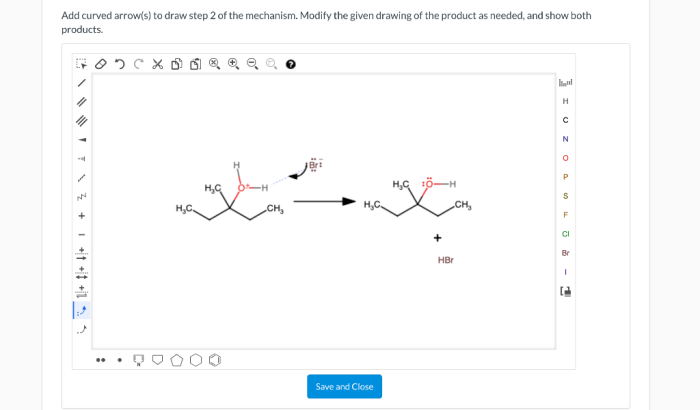
What is an appropriate stepwise synthesis for the reaction shown – Stepwise synthesis, a powerful technique in organic chemistry, involves constructing complex molecules through a series of discrete, sequential steps. This approach offers advantages and challenges, and selecting the appropriate stepwise synthesis pathway for a given reaction requires careful consideration. This article provides a comprehensive overview of stepwise synthesis, including its definition, guidelines for identifying the appropriate pathway, and strategies for optimization.
Stepwise synthesis offers several advantages over one-step synthesis, including greater control over the reaction process, higher yields, and the ability to incorporate functional groups and structural features in a controlled manner. However, it also has disadvantages, such as longer reaction times, the need for multiple purification steps, and potential side reactions.
1. Definition of Stepwise Synthesis
Stepwise synthesis is a synthetic approach that involves the sequential construction of a target molecule through a series of well-defined chemical reactions. Each reaction introduces a specific functional group or structural feature, gradually transforming the starting materials into the desired product.
Advantages of stepwise synthesis include:
- Allows for precise control over the reaction pathway and product selectivity.
- Enables the synthesis of complex molecules with high yields and purity.
- Provides opportunities for purification and characterization of intermediate products.
Disadvantages of stepwise synthesis include:
- Can be time-consuming and require multiple reaction steps.
- May involve the use of hazardous or expensive reagents.
- Can generate significant waste products.
2. Identifying the Appropriate Stepwise Synthesis
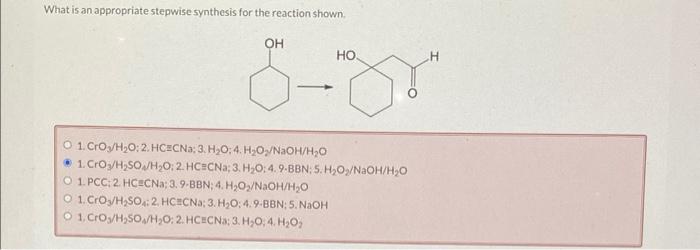
The choice of an appropriate stepwise synthesis pathway depends on several factors:
- Target molecule structure:The desired product’s complexity and functional group requirements influence the synthetic strategy.
- Availability of starting materials:The accessibility and cost of starting materials can limit the feasibility of certain pathways.
- Reaction efficiency and selectivity:The efficiency and selectivity of each reaction step impact the overall yield and purity of the final product.
- Functional group compatibility:The compatibility of functional groups present in the starting materials and intermediate products must be considered to avoid unwanted side reactions.
3. Example Stepwise Synthesis Pathways
| Reaction | Starting Materials | Intermediate Products | Final Product |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nucleophilic addition | Ketone, Grignard reagent | Alcohol | Ether |
| Electrophilic aromatic substitution | Benzene, electrophile | Arenium ion | Substituted benzene |
| Aldol condensation | Aldehyde or ketone | Enolate | β-Hydroxyaldehyde or β-hydroxyketone |
| Diels-Alder reaction | Diene, dienophile | Cyclic adduct | Cyclohexene or cyclopentene |
4. Methods and Procedures
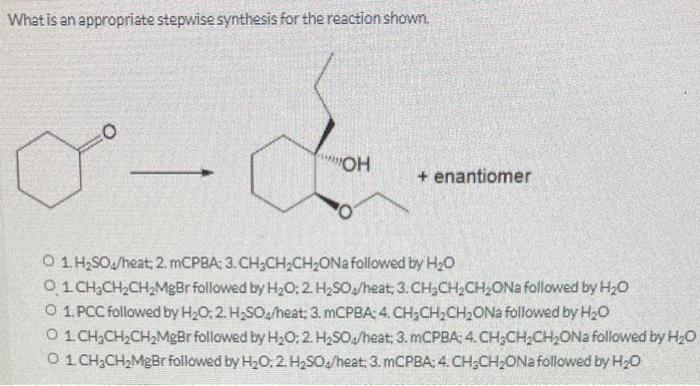
Stepwise synthesis involves the following general methods and procedures:
- Reaction setup:The starting materials, reagents, and solvents are combined in a reaction vessel under appropriate conditions.
- Reaction monitoring:The reaction progress is monitored using techniques such as thin-layer chromatography (TLC) or nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy.
- Purification:The reaction mixture is purified to isolate the desired product from impurities and byproducts.
- Characterization:The purified product is characterized using analytical techniques such as NMR, mass spectrometry, or infrared spectroscopy.
The flowchart below illustrates the typical steps in a stepwise synthesis process:
- Start
- Reaction setup
- Reaction monitoring
- Purification
- Characterization
- End
5. Optimization of Stepwise Synthesis: What Is An Appropriate Stepwise Synthesis For The Reaction Shown
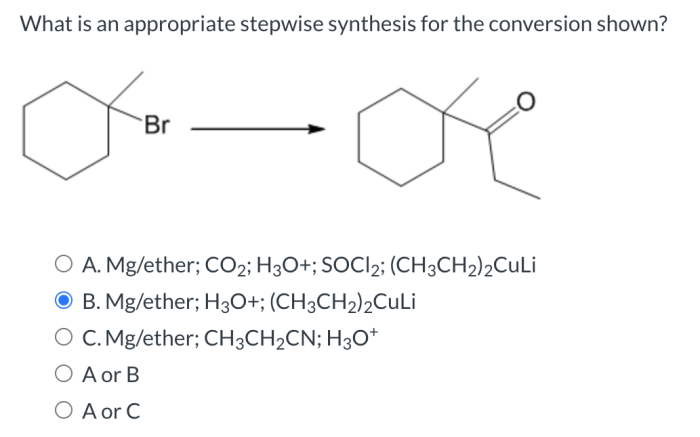
Optimizing stepwise synthesis reactions involves:
- Reaction conditions:Adjusting temperature, solvent, and reaction time to maximize yield and selectivity.
- Reagent selection:Choosing reagents that are compatible with the functional groups present and minimize side reactions.
- Purification techniques:Employing appropriate purification methods to effectively separate the desired product from impurities.
FAQs
What are the key factors to consider when choosing a stepwise synthesis pathway?
Factors to consider include the availability of starting materials, the reactivity of intermediates, the desired functional groups and structural features, and the potential for side reactions.
How can stepwise synthesis be optimized for efficiency and yield?
Optimization strategies include selecting appropriate reaction conditions, using efficient reagents, and employing effective purification techniques.
What are the advantages of stepwise synthesis over one-step synthesis?
Advantages include greater control over the reaction process, higher yields, and the ability to incorporate functional groups and structural features in a controlled manner.